NABARD GRADE A Exam: Your Gateway to a Fulfilling Career in Rural Development
The National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) is an apex development bank in India, focusing on rural and agricultural development. It plays a pivotal role in ensuring financial inclusion and rural prosperity in the country. If you're aspiring to make a difference in the lives of rural communities and seek a career that's both rewarding and impactful, the NABARD grade A exam is your gateway to success.
Understanding the NABARD grade a Exam (general)
The NABARD exam is a highly competitive examination that offers positions in various fields, including Rural Development Banking Service (RDBS), Grade A and Grade B officers, and Development Assistant. It's a comprehensive exam that tests candidates' knowledge in areas like agriculture, rural development, and finance.
Why NABARD?
Serving Rural India: Working with NABARD means you'll be actively contributing to the development of rural India. This career is not just a job but a mission to improve the lives of millions of people.
Diverse Career Opportunities: NABARD offers a wide range of career opportunities, from agricultural and rural banking to policymaking, research, and development projects. It's a platform that allows you to explore your interests and skills.
Stability and Benefits: NABARD offers a competitive salary, job security, and numerous benefits, making it an attractive career option.
How to Prepare for the NABARD GRADE A Exam ?
Understand the Syllabus: Begin by thoroughly understanding the exam syllabus. The NABARD exam covers topics such as agriculture, rural development, economics, and finance. Make sure to go through the official exam notification for specific details.
Quality Study Material: Invest in quality study materials, reference books, and online resources. Make a study plan and stick to it.
Practice Regularly: Practice is the key to success. Solve previous years' question papers and take online mock tests to get a feel for the exam pattern and time management.
Stay Updated: Keep yourself updated with current affairs, especially in the fields of agriculture, rural development, and economics.
Seek Guidance: Consider joining a coaching institute or an online course to receive guidance from experienced professionals and mentors.
Stay Healthy: Don't neglect your health during preparation. A healthy body and mind are essential for success.
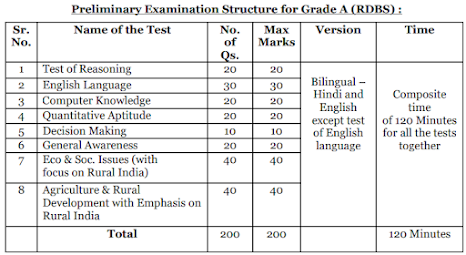
EXAM PATTERN FOR NABARD GRADE A :
PRE EXAM:
i) Qualifying Section - Test of Reasoning, English Language, Computer Knowledge, Quantitative Aptitude, Decision Making
ii) Merit Section - General Awareness, Eco & Soc. Issues (with focus on Rural India), Agriculture & Rural Development with Emphasis on Rural India.
iii) Shortlisting of the candidates for the Main exam will be based on marks scored in the Merit section only.
MAINS EXAM:
Syllabus for NABARD GRADE A EXAM 2023
Syllabus for reasoning , English , Quant and GA (current affairs/ general awareness) is similar to other banking exams.
Economic & Social Issues:
Nature of Indian Economy - Structural and Institutional features - Economic underdevelopment - Opening up the Indian Economy - Globalisation - Economic Reforms in India - Privatisation. Inflation - Trends in Inflation & their Impact on National Economy and Individual Income. Poverty Alleviation and Employment Generation in India - Rural and Urban - Measurement of Poverty - Poverty Alleviation Programmes of the Government. Population Trends - Population Growth and Economic Development - Population Policy in India. Agriculture - Characteristics / Status - Technical and Institutional changes in Indian Agriculture - Agricultural performance - Issues in Food Security in India - Non Institutional and Institutional Agencies in rural credit. Industry - Industrial and Labour Policy - Industrial performance - Regional Imbalance in India's Industrial Development - Public Sector Enterprises. Rural banking and financial institutions in India - Reforms in Banking/ Financial sector. Globalisation of Economy - Role of International Funding Institutions - IMF & World Bank - WTO - Regional Economic Co-operation. Social Structure in India - Multiculturalism - Demographic trends - Urbanisation and Migration - Gender Issues Joint family system - Social Infrastructure - Education - Health and Environment. Education - Status & System of Education - Socio -Economic Problems associated with Illiteracy - Educational relevance and educational wastage - Educational Policy for India. Social Justice: Problems of scheduled castes and scheduled tribes - socio-economic programmes for scheduled castes and scheduled tribes and other backward classes. Positive Discrimination in favour of the under privileged - Social Movements - Indian Political Systems - Human Development. Current Economic & Social Issues.
Agriculture & Rural Development:
Agriculture: definition, meaning and its branches, Agronomy: definition, meaning and scope of agronomy. Classification of field crops. Factors affecting on crop production, Agro Climatic Zones; Cropping Systems: Definition and types of cropping systems. Problems of dry land agriculture; Seed production, seed processing, seed village; Meteorology: weather parameters, crop-weather advisory; Precision Farming, System of Crop Intensification, organic farming;
a) Soil and Water Conservation : Major soil types, soil fertility, fertilisers, soil erosion, soil conservation, watershed management;
b) Water Resource: Irrigation Management: types of irrigation, sources of irrigation, crop-water requirement, command area development, water conservation techniques, micro-irrigation, irrigation pumps, major, medium and minor irrigation.
c) Farm and Agri Engineering : Farm Machinery and Power, Sources of power on the farm- human, animal, mechanical, electrical, wind, solar and biomass, bio fuels, water harvesting structures, farm ponds, watershed management, Agro Processing, Controlled and modified storage, perishable food storage, godowns, bins and grain silos. d) Plantation & Horticulture: Definition, meaning and its branches. Agronomic practices and production technology of various plantation and horticulture crops. Post-harvest management, value and supply chain management of Plantation and Horticulture crops.
e) Animal Husbandry: Farm animals and their role in Indian economy, Animal husbandry methods in India, common terms pertaining to different species of livestock, Utility classification of breeds of cattle. Introduction to common feeds and fodders, their classification and utility.
Introduction to poultry industry in India (past, present and future status), Common terms pertaining to poultry production and management. Concept of mixed farming and its relevance to socio-economic conditions of farmers in India. Complimentary and obligatory nature of livestock and poultry production with that of agricultural farming.
f) Fisheries: Fisheries resources, management and exploitation - freshwater, brackish water and marine; Aquaculture- Inland and marine; biotechnology; post-harvest technology. Importance of fisheries in India. Common terms pertaining to fish production.
g) Forestry: Basic concepts of Forest and Forestry. Principles of silviculture, forest mensuration, forest management and forest economics. Concepts of social forestry, agroforestry, joint forest management. Forest policy and legislation in India, India State of Forest Report 2015. Recent developments under Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
h) Agriculture Extensions: Its importance and role, methods of evaluation of extension programmes, Role of Krishi Vigyan Kendra's (KVK) in dissemination of Agricultural technologies.
i) Ecology and Climate Change: Ecology and its relevance to man, natural resources, their sustainable management and conservation. Causes of climate change, Green House Gases (GHG), major GHG emitting countries, climate analysis, distinguish between adaptation and mitigation, climate change impact to agriculture and rural
livelihood, carbon credit, IPCC, UNFCCC, CoP meetings, funding mechanisms for climate change projects, initiatives by Govt of India, NAPCC, SAPCC, INDC.
j) Present Scenario of Indian Agriculture and Allied activities; recent trends, major challenges in agriculture measures to enhance viability of agriculture. Factors of Production in agriculture; Agricultural Finance and Marketing; Impact of Globalization on Indian Agriculture and issues of Food Security; Concept and Types of Farm Management.
Rural Development:
Concept of Rural Area, Structure of the Indian Rural Economy-Importance and role of the rural sector in India- Economic, Social and Demographic Characteristics of the Indian rural economy, causes of rural backwardness.
Rural population in India; Occupational structure, Farmers, Agricultural Labourers, Artisans, Handicrafts, Traders, Forest dwellers/tribes and others in rural India- Trends of change in rural population and rural work force; problems and conditions of rural labour; Issues and challenges in Handlooms
Panchayati Raj Institutions – Functions and Working. MGNREGA, NRLM – Aajeevika, Rural Drinking water Programmes, Swachh Bharat, Rural Housing, PURA and other rural development programmes.
SALARY: (2023)
Pay Scale: Selected candidates will draw a starting basic pay of Rs.44,500/- p.m. in the scale of Rs. 44500 – 2500 (4) – 54500 – 2850 (7) – 74450 – EB – 2850 (4) – 85850 – 3300 (1) – 89150 (17 Years) applicable to Officers in Grade 'A' and they will be eligible for Dearness Allowance, Local Compensatory Allowance, House Rent Allowance, and Grade Allowance as per rules in force from time to time. At present, initial monthly gross emoluments are approximately Rs. 1,00,000.
ELIGIBILITY:
Bachelor’s Degree in any subject from any recognized University/Institution with a minimum of 60% marks (SC/ST/PWBD applicants - 55%) in aggregate OR Post Graduate degree, MBA/PGDM with a minimum of 55% marks (SC/ST/PWBD applicants - 50%) in aggregate OR CA/ CS/ICWA OR Ph.D from Institutions recognized by GOI/UGC.

Comments
Post a Comment